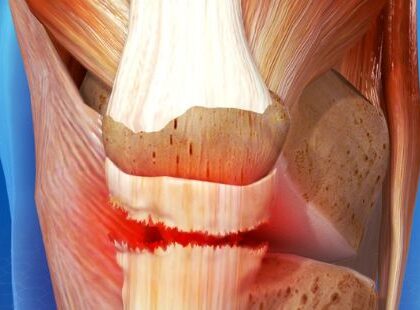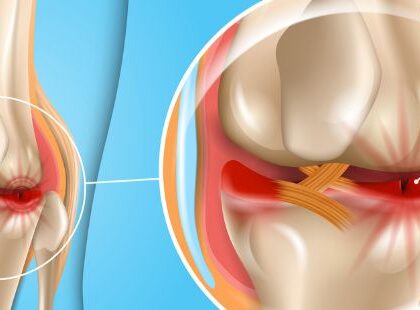
A bulging disc is one of the most common forms of spinal injuries. This is a condition caused by injury or damage of the intervertebral disc which are part of your spine.
What are Intervertebral Discs and why are they important?
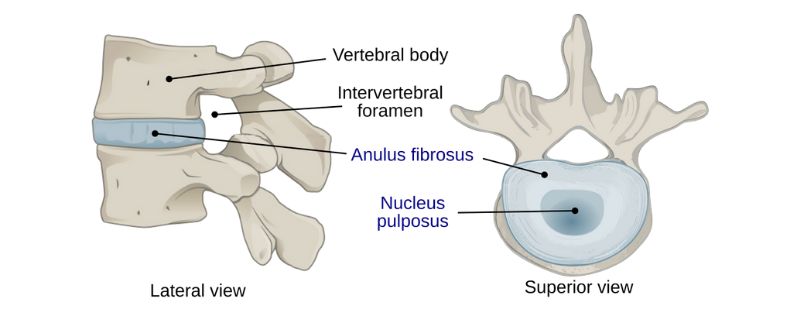
The bones of the spine (called vertebrae) are separated by fibrous discs. The purpose of these discs is to act as shock absorbers and force distributers between the vertebrae.
Intervertebral discs play a major role in the movement of your spine. The space that these discs create between the vertebrae allows for spinal nerves to pass between each segment of your spine.
The neck has the greatest range of movement. As we proceed down the spine, the vertebrae become bigger and thicker and anatomically have less movement. In the lower back, the intervertebral discs primarily act as shock absorbers and for weight distribution.
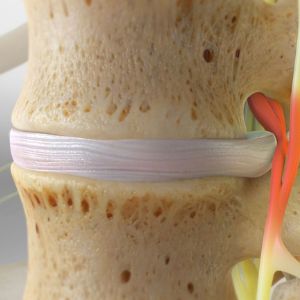
An Intervertebral Disc is comprised of two key elements
- The external Annulus Fibrosus (AF): The AF is a tough elastic-like outer band comprising of several layers of fibrocartilage packed densely together. This component provides the rigidity and stability to the intervertebral disc.
- The internal Nucleus Pulposus (NP): This is the soft centre of the disc made up of a thick gel-like substance. It can move and adapt within the annulus fibrosus to adjust to the pressures and forces placed on the spine.
What is a Bulging Disc?
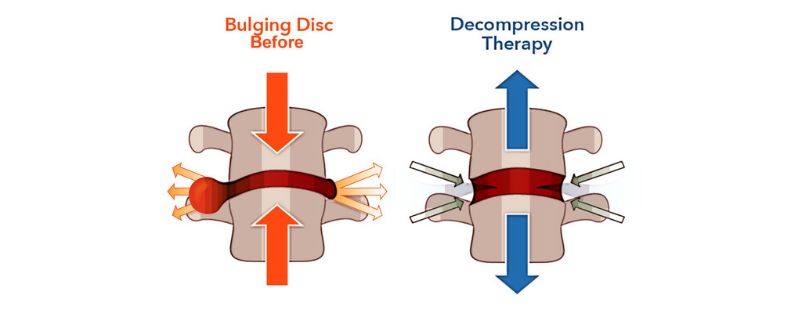
A bulging disc occurs when the structure of the intervertebral disc becomes damaged. This can happen in a few different ways, and these various types can also determine the severity of the condition.
These are some of the main types of bulging discs:
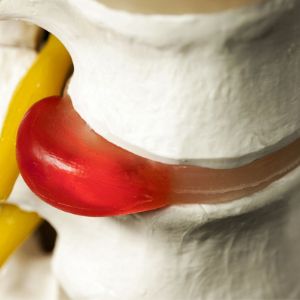
- The Annulus Fibrosus gets disfigured and distorted: Bulging discs can happen due damage of the AF. In this case the Nucleus Pulposus (NP) remains intact. The AF may or may not, impact on spinal nerves due to its disfiguration. This type of bulging disc may be asymptomatic; however, the individual may experience some stiffness and muscle spasm in the surrounding area.
- The Nucleus Pulposus (NP) gets disfigured: In this case though the AF may be relatively intact, it, along with AF, is disfigured. This might impact the spinal nerves, especially if the bulge is asymmetrical. This type of bulge is also known as a protrusion or a protruding disc.
- Ruptured Nucleus Pulposus. This is known as a herniated disc. It occurs when the outer Annulus Fibrosus is torn and the inner nucleus leaks out. It can end up pinching or irritating a nearby nerve, potentially resulting in pain, numbness or weakness of limbs.
It is also common to have asymptomatic bulging discs that are damaged, but does not cause any noticeable pain or discomfort.
What Causes a Bulging Disc?
Now that we know what bulging discs are, let’s look at what causes them, and how to treat them. We can classify the causes into 3 main categories.
- Sudden Onset of a Bulging Disc: This happens when sudden unexpected forces damage the disc. It could happen due to an accident or even due to an attempt to try and lift something heavy.
- Gradual Onset of a Bulging Disc: Sometimes repetitive stress or microtrauma can lead to disc damage over time. Some of the common causes include poor body posture or use of poor techniques in the gym.
Essentially, any activity that leads to incorrect positioning of your back over extended periods can lead to disc injuries. A gradual onset towards a disc injury is relatively common nowadays due to pressures of the modern lifestyle.
Genetic Predisposition & Age: As we age, our discs and our joints tend to degenerate. This can lead to disc bulging – symptomatic or asymptomatic – over time. Genetic factors can also account for a small percentage of bulging disc injury cases.
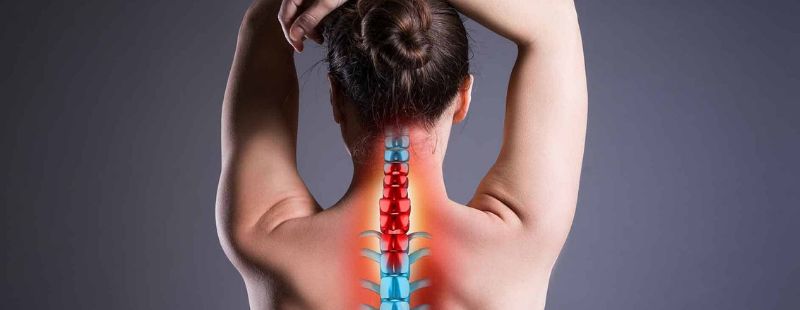
What are the Symptoms of Bulging Discs?
While in some cases of bulging disc injuries, people may not actually experience any noticeable symptoms, most cases are accompanied by at least some of the below symptoms.
- Localised intense pain
- Restricted movement
- Muscular spasm of the surrounding area
- Numbness of limbs
- Nerve pain – When any of your lumbar discs are affected, you can experience pain in your legs. This is called sciatica as the bulging disc affects the sciatic nerves causing pain. The nerves of the arm can also be affected in case of a cervical disc bulge.
- Altered bowel and bladder function.
- Stiffness of back
How to Treat a Bulging Disc
Most incidents of disc injury can be treated conservatively without the need for surgical intervention. However, in case of extreme damage, and an impact on the nerves, surgery is often the best option.
At Paramount Health we are committed to helping you lead an active and pain-free life. Get in touch with us, and our expert chiropractors will take you through the complete treatment process from initial pain relief to a complete rehabilitation plan to help you get back to your active life.
At times, bulging discs can cause severe pain. In such cases, our first focus will be on pain relief. Our team will help with the reduction of muscular spasm. This is often the main cause of pain when it comes to mild disc bulges.
You can get further relief by alternately applying ice and heat to the affected area and taking prescribed anti-inflammatories.
The treatment process includes relieving the localised muscular spasm, settling down any affected nerves, and removing any other pressure from the affected spinal segment.
Once the inflammation is down and some movement is restored, we can then look at exercise rehabilitation.
Our team will recommend a few gentle exercises that are suitable for you to safely do from home. We will also guide you on any exercise regime that you may be undertaking.
If you have ongoing low back pain, or have been suffering from bulging discs, feel free to contact us and we will help you get back to a pain-free life. You can also book an appointment by clicking here.
Bulging Disc is a condition that, if left untreated, can lead to severe debilitating pain and other health complications. If identified quickly, and with proper medical help, you can get back to your normal life – usually within a few weeks’ time.